Glycerin, the commercial name for glycerol, is the basic backbone for glycerides that can be naturally found in living organisms. As a raw material, it has a wide range of uses in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, fuel, and many more. However, the chemical is also used in the food industry as a sweetener, emulsifier, and stabilizer. Being in so many products that vegans could eat and use, it is important to determine whether the ingredient is vegan or not.
Glycerin is considered a gray area because while it is predominantly produced from plant oils, it can also be produced from animal fats. If a food product contains glycerin in its ingredients list, it is difficult to determine if the glycerin was produced from plant or animal sources. Some vegans find comfort if the ingredient is listed as “vegetable glycerin,” but that label in itself also comes with a few issues.
Table of Contents
Glycerin
Glycerin is a simple polyol – a substance that contains multiple hydroxyl groups. Specifically, glycerin has three hydroxyl groups, making it a triol. In biochemistry, the structure is incredibly important as it serves as the backbone in the groups of lipids called glycerides (e.g., monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, etc.) (1).
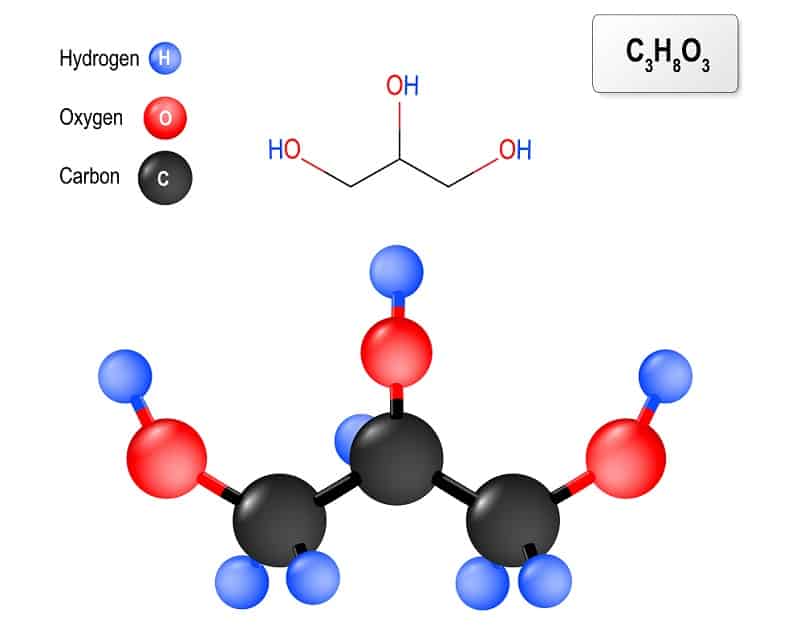
Glycerin is often confused with glycerine and glycerol. To help clear things up, glycerol is the specific name of the chemical. However, glycerin and glycerine are common commercial names used in the US to refer to a product that is composed of about 95% or more glycerol.
Due to the structural simplicity of glycerin, it has been found to be used in a wide array of applications. Aside from the food industry, glycerin is also heavily used in medications, personal care products, cosmetics, botanical tinctures, electronic cigarette liquids, antifreeze, and many more. Glycerin is also used as a chemical intermediate for more complex substances such as nitroglycerin – the essential ingredient in explosives such as dynamite.
The wide range of uses for glycerin stem from its structural simplicity and its varied chemical properties. For one, glycerin is an excellent solvent as it can help dissolve both polar and nonpolar substances. As a solvent, glycerin is used in many manufacturing industries.
Glycerin is also a humectant, a substance that helps keep moisture levels maintained. As a humectant, glycerin is extensively used in both cosmetics (i.e., in moisturizers, soaps, topical creams, etc.) and in the food industry (i.e., to control viscosity and texture).
As a sugar alcohol, glycerin can even be used in the food industry as a sweetener. While glycerin is only estimated to be about 60% as sweet as table sugar, it specifically does not feed the microorganisms that cause dental cavities.
Is Glycerin Vegan?

Glycerin is primarily produced using plant oils from soybeans and palm. However, it can also be derived from animal fats. Food manufacturers often source raw ingredients from other companies which means a food product contains ingredients obtained from different manufacturers. This makes it difficult to pinpoint whether the glycerin used by a food manufacturer is vegan or not.
Thus, it is difficult to determine whether glycerin is vegan or not. It can be considered a gray area ingredient at best.
Manufacturers sometimes label glycerin as “vegetable glycerin.” If that is the name used in the ingredients list, then that means that the glycerin used in that food product has been derived from plant sources and is in fact vegan.
While vegetable glycerin can already be considered vegan, especially for dietary vegans, there are some that might still take issue with vegetable glycerin sourced from palm oil. Environmental vegans stand firm against the palm oil industry because studies have shown that extensive palm plantations have been prioritized over pristine forestland, contributing to the significant loss of forest cover on the planet.
Glycerin Production
There are different ways to produce glycerol. Firstly, it can be extracted from natural sources such as animal fats or plant oils. Secondly, it can also be synthesized.
From natural fats and oils, triglycerides can be converted to glycerin through a process called saponification. The process refers to the conversion of fats, oils, or lipids into soap and alcohol. Specifically, the triglyceride will be saponified using sodium hydroxide and water. The simple equation will then yield three soaps and one glycerol molecule.
Triglycerides can also be hydrolyzed to produce crude glycerol. However, this process requires further purification with activated carbon to remove organic impurities.
Triglycerides used in glycerin production often come from plant sources, typically from soybeans and palm. However, animal-derived sources such as tallow (i.e., a rendered form of fat) can also be used for glycerin production.
Instead of converting a natural triglyceride, glycerin can also be synthesized using propene as the base structure. The propene is first chlorinated and then subsequently oxidized with hypochlorite. The final product is then hydrolyzed to produce glycerol.
Food that Contains Glycerin
Since glycerin serves numerous purposes in the food industry, it should come as no surprise that the ingredient can be found in a wide array of food products.
Glycerin can be found in nutrition and energy bars, various drinks, cake icings, ice cream, confectionery, precooked pasta, rolled oats, breakfast cereals, rice or tapioca pudding, soft candies, chewing gum, condiments, diet foods, dried fruits and vegetables, marshmallows, soups, spices, and seasonings.
Is Glycerin Safe?
Used in different industries, people have concerns if whether the ingredient used in applications such as vehicle antifreeze is also safe to consume. However, various food safety authorities have set the necessary standards to make sure that glycerin in food products is safe for human consumption.
The JEFCA (Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives) evaluated glycerin back in 2002 (2). With no safety concerns, the group recognizes the many uses of glycerin in the food industry such as a flavoring agent, carrier solvent, emulsifier, humectant, and thickener.
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) also has no issue with glycerin as long as it follows good manufacturing practices (3). Passing internal standards and using safety studies, the FDA considers glycerin as GRAS (generally recognized as safe).
Also using various safety studies and evidence, the EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) concludes that glycerin does not raise any concern for genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and reproductive and prenatal development (4). Since the ingredient does not raise much safety concern, the group concluded that there is no need for an acceptable daily intake (ADI; the maximum amount a person can take daily for a year without any adverse health effects) value for glycerin.
References




